Mean Square Displacement¶
To determine the self diffusion
coefficient \(D_A\) of
particles of type \(A\), one can use the Einstein
relation 108:
(1)¶\[\lim_{t \rightarrow \infty} \langle \|{\bf r}_i(t) - {\bf r}_i(0)\|^2 \rangle_{i \in A} ~=~ 6 D_A t\]
This mean square displacement and \(D_A\) are calculated by the
program gmx msd. Normally
an index file containing atom numbers is used and the MSD is averaged
over these atoms. For molecules consisting of more than one atom,
\({\bf r}_i\) can be taken as the center of mass positions of the
molecules. In that case, you should use an index file with molecule
numbers. The results will be nearly identical to averaging over atoms,
however. The gmx msd program can also be used for
calculating diffusion in one or two dimensions. This is useful for
studying lateral diffusion on interfaces.
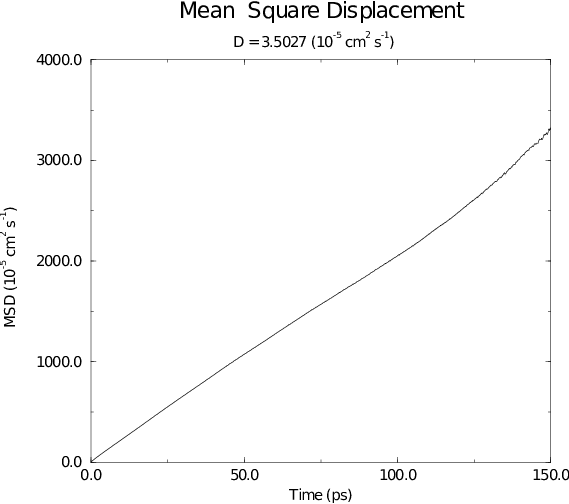
An example of the mean square displacement of SPC water is given in Fig. 54.