Radial distribution functions#
with \(\langle\rho_B(r)\rangle\) the particle density of type \(B\) at a distance \(r\) around particles \(A\), and \(\langle\rho_B\rangle_{local}\) the particle density of type \(B\) averaged over all spheres around particles \(A\) with radius \(r_{max}\) (see Fig. 52 C).
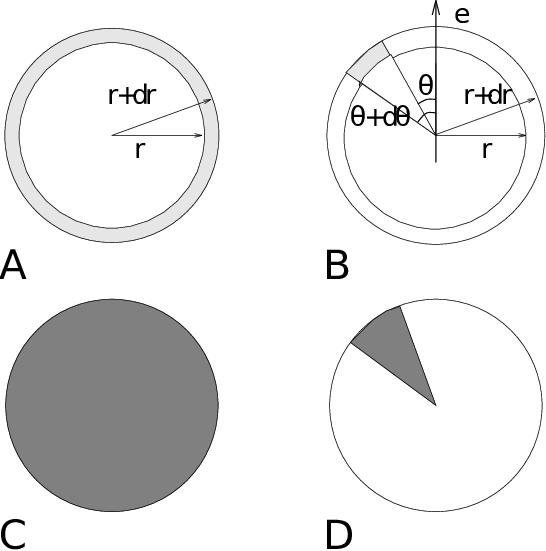
Fig. 52 Definition of slices in gmx rdf: A. \(g_{AB}(r)\). B. \(g_{AB}(r,\theta)\). The slices are colored gray. C. Normalization \(\langle\rho_B\rangle_{local}\). D. Normalization \(\langle\rho_B\rangle_{local,\:\theta }\). Normalization volumes are colored gray.#
Usually the value of \(r_{max}\) is half of the box length. The averaging is also performed in time. In practice the analysis program gmx rdf divides the system into spherical slices (from \(r\) to \(r+dr\), see Fig. 52 A) and makes a histogram in stead of the \(\delta\)-function. An example of the RDF of oxygen-oxygen in SPC water 80 is given in Fig. 53
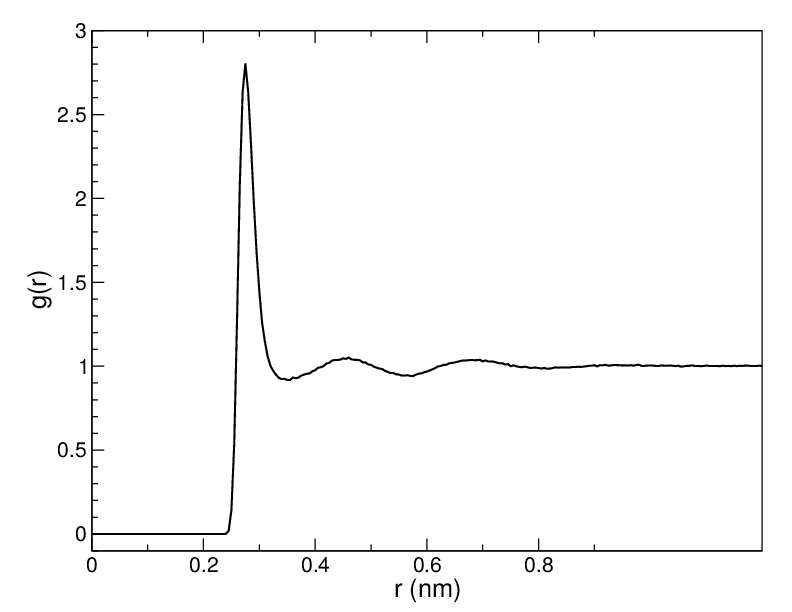
Fig. 53 \(g_{OO}(r)\) for Oxygen-Oxygen of SPC-water.#
With gmx rdf it is also possible to calculate an angle dependent rdf \(g_{AB}(r,\theta)\), where the angle \(\theta\) is defined with respect to a certain laboratory axis \({\bf e}\), see Fig. 52 B.
This \(g_{AB}(r,\theta)\) is useful for analyzing anisotropic systems. Note that in this case the normalization \(\langle\rho_B\rangle_{local,\:\theta}\) is the average density in all angle slices from \(\theta\) to \(\theta + d\theta\) up to \(r_{max}\), so angle dependent, see Fig. 52 D.