|
Gromacs
2024.1
|
|
Gromacs
2024.1
|
 Collaboration diagram for Framework for Energy Analysis (energyanalysis):
Collaboration diagram for Framework for Energy Analysis (energyanalysis):Provides functionality for implementing energy analysis modules.
This module implements a framework for implementing flexible energy analysis routines. It provides a base class for implementing analysis as reusable modules that can be used from different contexts and can also support per-frame parallelization. It integrally uses functionality from the following modules:
The main interface of this module is the gmx::EnergyAnalysisModule class. Analysis modules should derive from this class, and override the necessary virtual methods to provide the actual initialization and analysis routines. gmx::EnergyAnalysisModuleData can be used in advanced scenarios where the tool requires custom thread-local data for parallel analysis.
The sequence charts below provides an overview of how the energy analysis modules typically interact with other components. The first chart provides an overview of the call sequence of the most important methods in gmx::EnergyAnalysisModule. There is a runner, which is responsible for doing the work that is shared between all energy analysis (such as reading the energy files). The runner then calls different methods in the analysis module at appropriate points to perform the module-specific tasks. The analysis module is responsible for creating and managing gmx::AnalysisData objects, and the chart shows the most important interactions with this module as well. However, the runner takes responsibility of calling gmx::AnalysisData::finishFrameSerial(). Interactions with options (for command-line option processing) and selections is not shown for brevity: see Extensible Handling of Options (options) for an overview of how options work, and the second chart for a more detailed view of how selections are accessed from an analysis module.
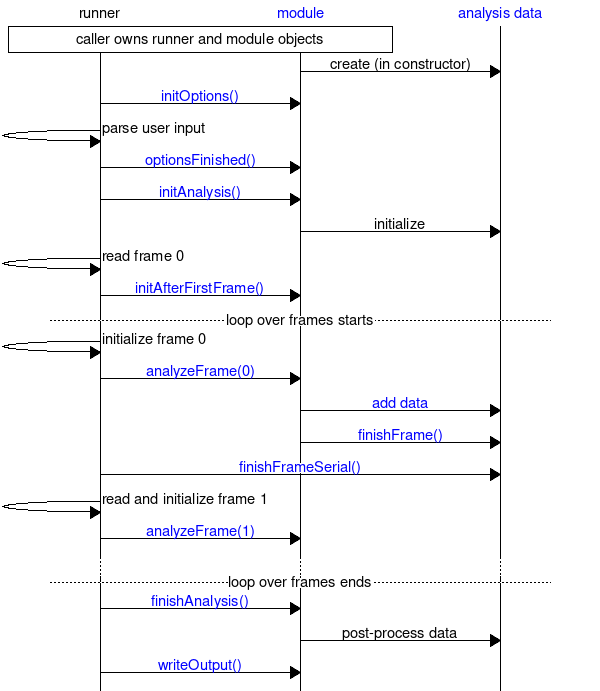
The final chart shows the flow within the frame loop in the case of parallel (threaded) execution and the interaction with the Parallelizable Handling of Output Data (analysisdata) module in this case. Although parallelization has not yet been implemented, it has influenced the design and needs to be understood if one wants to write modules that can take advantage of the parallelization once it gets implemented. The parallelization takes part over frames: analyzing a single frame is one unit of work. When the frame loop is started, gmx::EnergyAnalysisModule::startFrames() is called for each thread, and initializes an object that contains thread-local data needed during the analysis. This includes selection information, gmx::AnalysisDataHandle objects, and possibly other module-specific variables. Then, the runner reads the frames in sequence and passes the work into the different threads, together with the appropriate thread-local data object. The gmx::EnergyAnalysisModule::analyzeFrame() calls are only allowed to modify the thread-local data object; everything else is read-only. For any output, they pass the information to gmx::AnalysisData, which together with the runner takes care of ordering the data from different frames such that it gets processed in the right order. When all frames are analyzed, gmx::EnergyAnalysisModule::finishFrames() is called for each thread-local data object to destroy them and to accumulate possible results from them into the main gmx::EnergyAnalysisModule object. Note that in the diagram, some part of the work attributed for the runner (e.g., evaluating selections) will actually be carried out in the analysis threads before gmx::EnergyAnalysisModule::analyzeFrame() gets called.
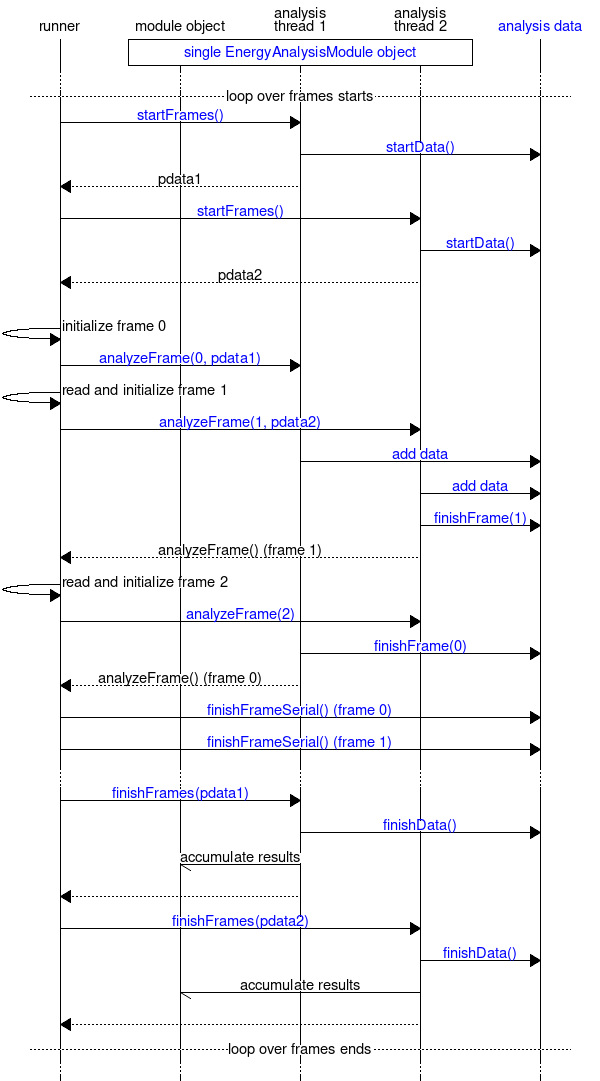
In addition to the framework for defining analysis modules, this module also provides gmx::EnergyAnalysisCommandLineRunner, which implements a command-line program that runs a certain analysis module.
Internally, the module also defines a set of trajectory analysis modules that can currently be accessed only through gmx::registerEnergyAnalysisModules.
Files | |
| file | analysismodule.h |
| Public API convenience header for energy analysis framework. | |
 1.8.5
1.8.5